Geocast: Difference between revisions
m →Applications: change |id={{citeseer}} to |citeseerx= using AWB |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | #UCB_CommandLine |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Sending a message to all computers on a network in a geographic location}} |
|||
{{original research|date=July 2021}} |
|||
[[Image:Geocast.svg|right|200px]] |
[[Image:Geocast.svg|right|200px]] |
||
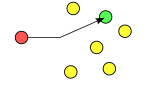
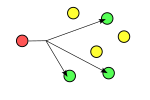
'''Geocast''' refers to the delivery of information to a |
'''Geocast''' refers to the delivery of information to a subset of destinations in a wireless peer-to-peer network identified by their geographical locations. It is used by some [[mobile ad hoc network]] routing protocols, but not applicable to Internet routing. |
||
==Geographic addressing== |
==Geographic addressing== |
||
{{Routing scheme}} |
{{Routing scheme}} |
||
A geographic destination address is expressed in three ways: point, circle (with center point and radius), and polygon (a list of points, e.g., P(1), P(2), |
A geographic destination address is expressed in three ways: point, circle (with center point and radius), and polygon (a list of points, e.g., P(1), P(2), ..., P(n–1), P(n)). A geographic router (Geo Router) calculates its service area (geographic area it serves) as the union of the geographic areas covered by the networks attached to it. This service area is approximated by a single closed polygon. Geo Routers exchange service area polygons to build routing tables. The routers are organized in a hierarchy. |
||
==Applications== |
==Applications== |
||
Geographic addressing and routing has many potential applications in geographic messaging, geographic advertising, delivery of geographically restricted services, and presence discovery of a service or mobile network participant in a limited geographic area.<ref>{{cite book |
Geographic addressing and routing has many potential applications in geographic messaging, geographic advertising, delivery of geographically restricted services, and presence discovery of a service or mobile network participant in a limited geographic area (see Navas, [[Tomasz Imieliński|Imieliński]], 'GeoCast - Geographic Addressing and Routing'.<ref>{{cite book | first1=J.C. |last1=Navas | first2=T. | last2=Imieliński|title=Proceedings of the 3rd annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking - MobiCom '97 |chapter=GeoCast---geographic addressing and routing |date= 1997|pages=66–76|doi=10.1145/262116.262132 |isbn=0897919882 |s2cid=17662140 |url=https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=fEYp6hEAAAAJ&citation_for_view=fEYp6hEAAAAJ:IjCSPb-OGe4C}}</ref>) |
||
|citeseerx = 10.1.1.102.8784 |
|||
|author=J.C. Navas, T. Imielinski |
|||
|title=GeoCast - Geographic Addressing and Routing |
|||
|work=Proceedings of the 3rd annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking |
|||
|location=Budapest, HU |
|||
|pages=66–67 |
|||
|year=1997 |
|||
|ISBN=0-89791-988-2 |
|||
|publisher=Association of Computing Machinery |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[Anycast]] |
|||
*[[Geographic routing]] |
|||
*[[Abiding Geocast / Stored Geocast]] |
*[[Abiding Geocast / Stored Geocast]] |
||
*[[Routing]] |
|||
*[[Unicast]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 31: | Line 19: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* RFC 2009 GPS-Based Addressing and Routing |
* RFC 2009 GPS-Based Addressing and Routing |
||
* [http://www.comsoc.org/livepubs/surveys/public/2004/apr/maihofer.html A Survey of Geocast Routing Protocols] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20040824083215/http://www.comsoc.org/livepubs/surveys/public/2004/apr/maihofer.html A Survey of Geocast Routing Protocols] |
||
* [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316921061_DCCast_Efficient_Point_to_Multipoint_Transfers_Across_Datacenters Efficient Point to Multipoint Transfers Across Datacenters] |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Ad hoc routing protocols]] |
||
[[Category:Internet broadcasting]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 17:30, 24 August 2023
This article possibly contains original research. (July 2021) |

Geocast refers to the delivery of information to a subset of destinations in a wireless peer-to-peer network identified by their geographical locations. It is used by some mobile ad hoc network routing protocols, but not applicable to Internet routing.
Geographic addressing[edit]
| Routing schemes |
|---|
| Unicast |
| Broadcast |
| Multicast |
| Anycast |
A geographic destination address is expressed in three ways: point, circle (with center point and radius), and polygon (a list of points, e.g., P(1), P(2), ..., P(n–1), P(n)). A geographic router (Geo Router) calculates its service area (geographic area it serves) as the union of the geographic areas covered by the networks attached to it. This service area is approximated by a single closed polygon. Geo Routers exchange service area polygons to build routing tables. The routers are organized in a hierarchy.
Applications[edit]
Geographic addressing and routing has many potential applications in geographic messaging, geographic advertising, delivery of geographically restricted services, and presence discovery of a service or mobile network participant in a limited geographic area (see Navas, Imieliński, 'GeoCast - Geographic Addressing and Routing'.[1])
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ Navas, J.C.; Imieliński, T. (1997). "GeoCast---geographic addressing and routing". Proceedings of the 3rd annual ACM/IEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking - MobiCom '97. pp. 66–76. doi:10.1145/262116.262132. ISBN 0897919882. S2CID 17662140.
External links[edit]
- RFC 2009 GPS-Based Addressing and Routing
- A Survey of Geocast Routing Protocols
- Efficient Point to Multipoint Transfers Across Datacenters